OpenAI Unveils Its Innovative Deep Research Tool in ChatGPT
In a dynamic response to the emergence of Deepseek, OpenAI has introduced a groundbreaking Deep Research feature within ChatGPT. This latest addition to OpenAI’s range of Agentic AI capabilities—following the earlier launch of Operator—signifies a significant leap toward enhancing AI independence. OpenAI asserts that the Deep Research functionality is equipped to generate comprehensive reports that rival the insights of seasoned research analysts, effectively interpreting and navigating the internet on the user’s behalf.
Utilizing OpenAI’s advanced o3 reasoning model, this feature is adept at tackling intricate tasks, albeit at a measured pace. Currently, it is accessible to ChatGPT Pro subscribers—a premium service priced at $200 per month—but it is slated for future availability among ChatGPT Plus and Enterprise users.
Understanding How OpenAI’s Deep Research AI Agent Operates
OpenAI’s Deep Research tool is built for autonomous operation. Upon receiving a thorough prompt, it seeks clarification through additional questions before delving into its analysis. The process typically ranges from 5 to 30 minutes, although the system claims to accomplish several hours of intensive human research within a remarkably short duration.
During its operation, users can view a live panel on the right side of their screen, displaying the AI’s ongoing tasks. This feature not only serves as a means of citation but also allows users to follow the AI’s reasoning. The AI can connect to the web, conduct searches, read articles, and synthesize vast amounts of information, including text, images, and PDFs. However, due to the high computational demand, OpenAI limits Pro users to 100 queries per month, with plans to introduce a streamlined model in the near future.
Applications of Deep Research
This innovative Deep Research feature is particularly advantageous for professionals in sectors such as science, finance, engineering, and policy-making. OpenAI emphasizes its versatility, noting the potential benefits for everyday users as well. For instance, the tool can conduct personalized research to assist with significant purchasing decisions—helping consumers compare products like vehicles, furniture, and gadgets. By aggregating insights from countless reviews and articles, it can generate tailored reports based on specific user requirements.
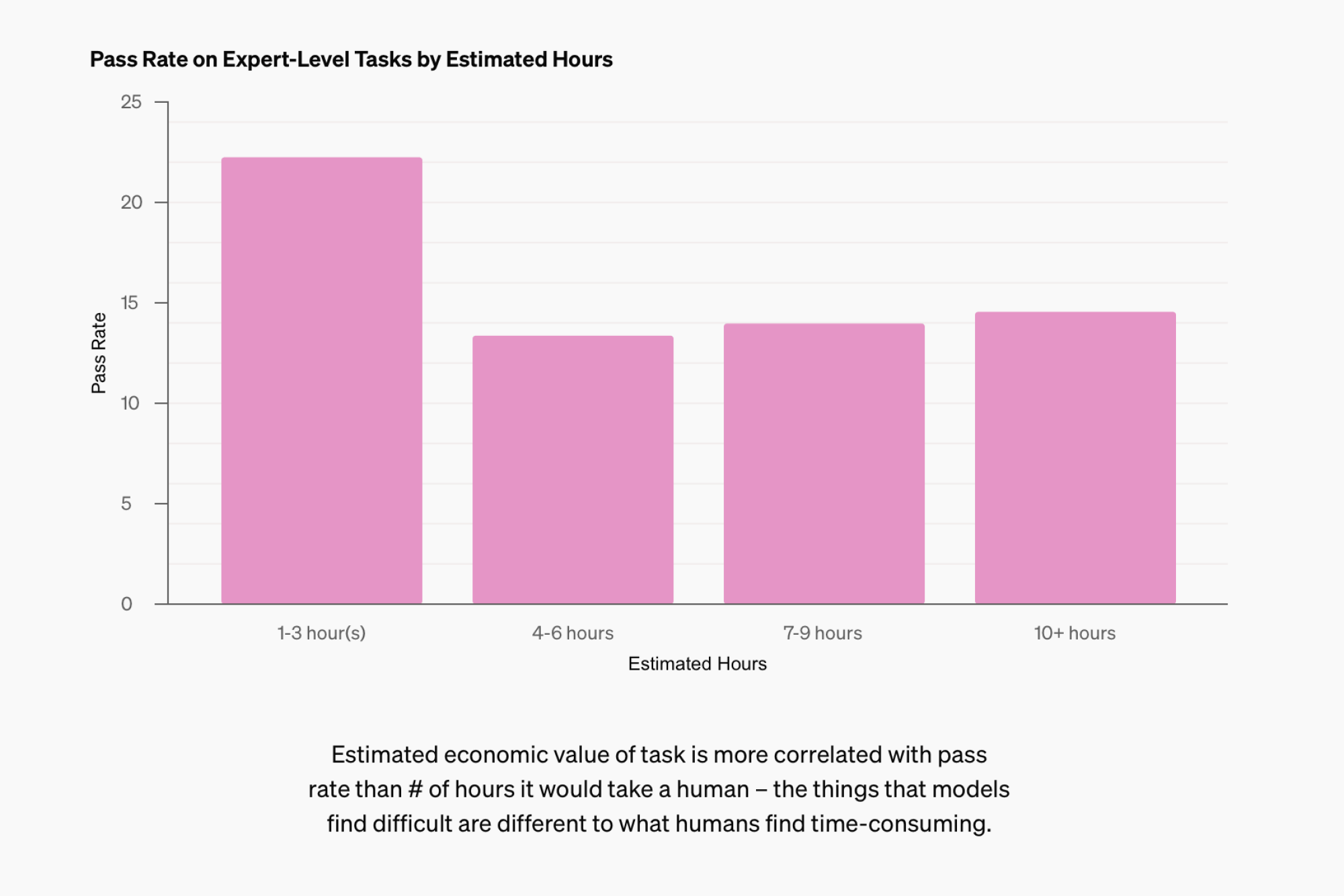
OpenAI reports that “deep research has been validated by experts as capable of automating intricate manual inquiries over several hours.” Numerous instances showcase how Deep Research can significantly reduce the time users spend conducting research, addressing highly specialized topics through extensive scientific literature.
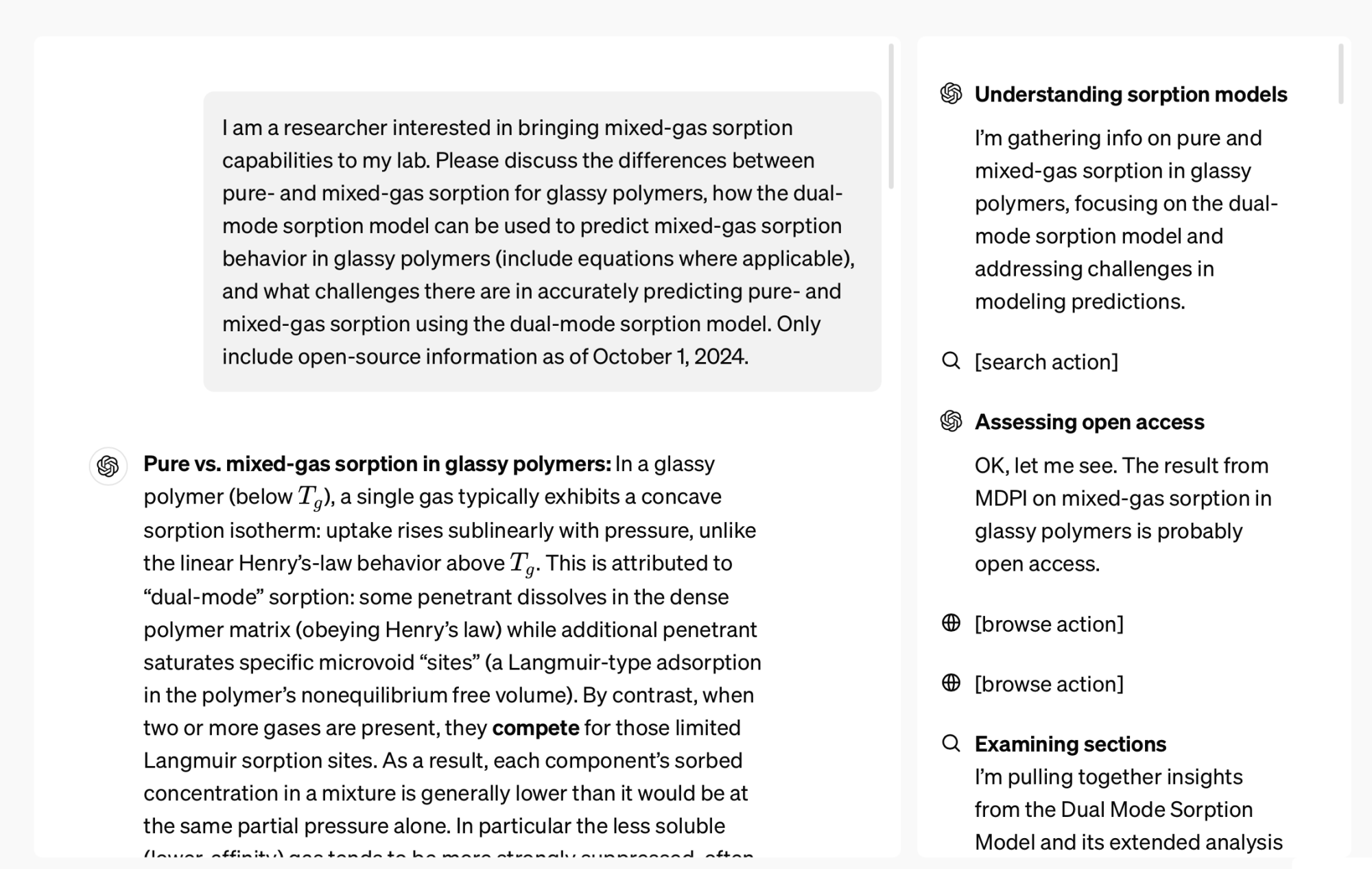
For example, when tasked with a detailed Chemistry inquiry—such as “compare pure- and mixed-gas sorption for glassy polymers and explain how the dual-mode sorption model predicts mixed-gas behavior”—the AI adeptly reviews relevant models, accesses a wealth of open-source data, clarifies key questions, retrieves PDFs, and synthesizes the findings, resulting in time savings of four hours, according to OpenAI.
Additionally, similar applications for Deep Research have been noted within healthcare and linguistics, providing significant time efficiencies of five hours and two hours, respectively.
In testing scenarios such as Humanity’s Last Exam, an AI benchmark assessing expertise across a range of fields, Deep Research achieved an impressive accuracy rate of 26.6%, the highest recorded score thus far. For context, DeepSeek-R-1 yielded a mere 9.4% accuracy, while GPT-4o fell to just 3.3%.
Monitoring Output and Reliability
While Deep Research leverages a reasoning model as its core mechanism, it still integrates a language model to process inputs and produce textual outputs. OpenAI cautions users that, despite its advancements, the Deep Research model may still hallucinate or generate inaccuracies, underscoring the importance of reviewing its findings carefully rather than accepting them at face value.